Advertisement
Machines have been getting better at understanding language, but that’s just one piece of the puzzle. We rarely think or communicate in just words. We react to images, tone, pacing, body language, and sound. Reka Core model seems to understand that. It isn't focused on text alone—it's built to understand visuals, audio, and even video right alongside the written word. That makes it more than just a text tool—it's something closer to a system that actually pays attention.
This doesn't mean it's just stacking abilities. The core isn't a collection of tools working side-by-side. It’s one model trained to process and connect multiple kinds of input all at once. That’s where the shift really happens.
Older models worked in silos. You fed them a text, and they responded with a text. Did you want image recognition? That was a separate tool. Video or audio? Another one again. Core handles all these in one space, with shared reasoning across formats. You can give it a clip, a caption, and a chart—and it processes them together, not separately.
Let’s say you show it a short video of someone walking through a busy intersection while talking. Core picks up the facial expressions, the background sounds, the rhythm of the speech, and the words being used. It doesn’t describe each part on its own. Instead, it figures out how they relate. Maybe the person sounds calm, but the traffic is chaotic. That kind of contrast might matter—and Core catches it.
This ability to interpret context across formats is what separates a model like Core from single-track systems. It doesn't guess based on one detail. It reads the situation all at once.
The strength of Core is in how it brings different types of data into one shared understanding. No matter what the input is—a sentence, a screenshot, a voice note—it translates that into a format the model can reason with. That’s how it sees connections and relationships between things that would feel unrelated to most systems.
Here’s how that plays out in practice:
Text paired with visuals: Feed it a tweet with a meme or a slide from a presentation. Core doesn't just summarize the text—it understands how the image adds (or changes) the meaning.

Video plus sound: Show it a news clip or an interview. It notices not only what's said but how it's said—whether the tone is defensive, if there's music setting a mood, or if someone offscreen reacts in a way that matters.
Audio with context clues: If you give it a voice message recorded in a noisy space, it can pick up on environmental clues. Not just “what was said,” but where it happened, how the speaker felt, and how confident they sounded.
Because all these forms of input land in the same internal system, Core doesn’t just guess—it reasons. That’s a big change from models that bolt together separate processors for text, vision, and audio.
When you work with Core, you don’t have to think about how to format your request. You just upload, type, or record. It handles the rest. That makes the experience smooth and surprisingly natural. It adjusts itself to the way you provide input rather than forcing you to adapt to its structure.
This makes a difference in real-world use. If you’re analyzing product feedback, for example, people might leave reviews as voice notes, images, or a mix of both. Core can process the tone of the voice, the emotion behind it, and any visual attachments—all at once. You don’t have to clean or separate the data first.
It's the same for training videos, support calls, or any situation where humans use a mix of cues to express what they mean. Core responds in a way that suggests it understands what's going on—not just the data but the setting, the emotion, and the intent behind it.
And it works fast. Multimodal models often slow down when handling more complex input, but Core has been built with efficiency in mind. It responds quickly, even with layered input. That kind of balance—depth without lag—is hard to find.

You can start by feeding Core any type of input—a video with background noise, a screenshot with overlapping text, or a mixed-media report. There's no need to clean up the files or convert them. Core processes them directly.
Once the input is in, you can ask specific questions like:
It’s not just about summarizing or describing. Core interprets intent, tone, and relationships between elements across different formats.
The responses adapt to the content. It might return a video breakdown with emotion tags at specific moments or generate organized notes from a cluttered visual layout. It adjusts to the kind of material you provide and the depth of the request.
You can also build on previous interactions. If you begin with a summary, you can follow up with a tone analysis or ask for further insights without needing to repeat the input. Core keeps track of the conversation flow.
Reka Core doesn’t try to impress with just size or speed. It’s the way it processes everything at once that makes it different. One model, multiple formats, and a shared understanding—that’s what gives it a sense of fluid intelligence. You don’t feel like you’re switching tools when you switch input types. It all stays connected.
This isn’t about gimmicks or patching together capabilities. It’s a cleaner, more intuitive way to interact with data that looks, sounds, and reads differently. If your work or research crosses those lines, Core makes it feel like you’re finally speaking the same language—no matter the format.
Advertisement

Discover Reka Core, the AI model that processes text, images, audio, and video in one system. Learn how it integrates multiple formats to provide smart, contextual understanding in real-time

AI is used in the beauty and haircare industry for personalized product recommendations and to improve the salon experience

Curious how Stable Diffusion 3 improves your art and design work? Learn how smarter prompts, better details, and consistent outputs are changing the game

Learn how to make your custom Python objects behave like built-in types with operator overloading. Master the essential methods for +, -, ==, and more in Python

Want to run LLaMA 3 on your own machine? Learn how to set it up locally, from hardware requirements to using frameworks like Hugging Face or llama.cpp
How to supercharge your AI innovation with the cloud. Learn how cloud platforms enable faster AI development, cost control, and seamless collaboration for smarter solutions

Build scalable AI models with the Couchbase AI technology platform. Enterprise AI development solutions for real-time insights

Wondering how databases stay connected and make sense? Learn how foreign keys link tables together, protect data, and keep everything organized

Learn how ThoughtSpot's AI agent, Spotter, revolutionizes conversational BI for smarter and more accessible business insights

Curious how IBM's Granite Code models help with code generation, translation, and debugging? See how these open AI tools make real coding tasks faster and smarter
Understand here how embedding models power semantic search by turning text into vectors to match meaning, not just keywords
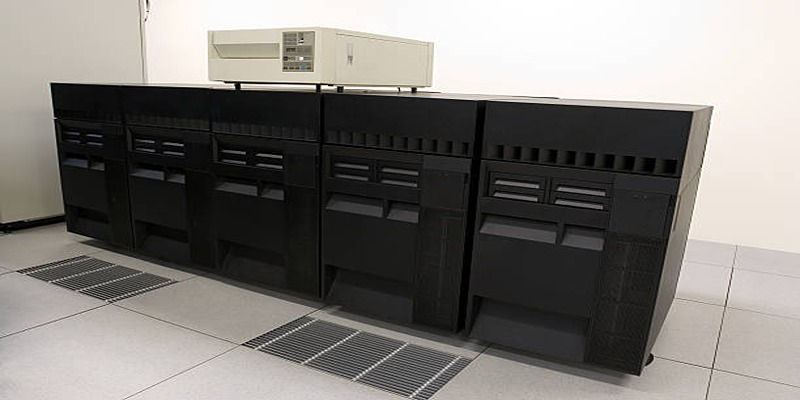

The IBM z15 empowers businesses with cutting-edge capabilities for hybrid cloud integration, data efficiency, and scalable performance, ensuring optimal solutions for modern enterprises.